You can access the paper via the examinations.ie website. No marking scheme is available at the time of writing. You may also like: Leaving Cert Biology.
Q1. (a) 1. To receive energy for cellular reactions to occur
2. For growth and repair
(b) Many sugar units joined together
(c) Cellulose
(d) Contains glycerol and three fatty acids
(e) Phospholipids are found in cell membranes
(f) Biuret test
Q2. (a) Living factor
(b) The place where an organism lives
(c) All of the different populations living in an area
(d) All members of the same species living in an area
(e) The functional role of an organism in an ecosystem
(f) The part of the Earth that sustains life
(g) Checking for the presence or absence of an organism in an ecosystem
Q3. (a) Interphase
(b) Cell division in which one cell becomes two cells and the number of chromosomes is retained. The genetic material of the daughter cell is identical to the mother cell.
(c) 1. The chromosome number is halved in meiosis
2. Meiosis involves 2 cell divisions, while mitosis only involves one
(d) The uncontrolled rate of mitosis
Q4. (a) The alteration of genes
(b) 1. Isolation
2. Cutting
3. Transformation
4. Expression
(c) Isolation: DNA is extracted from the organism
Expression: a product is made from the new DNA
(d) Plasmid
(e) Animal: the gene for blood clotting is inserted into sheep. The sheep produce clotting proteins in their milk that is needed for haemophiliacs.
Plant: golden rice is used to prevent vitamin A deficiency
Microorganism: bacteria are used to produce humulin, which is used as insulin in diabetics
Q5. (a) A growth regulator in plants
(b)(i) Meristems in root tips and shoot tips
(ii) Abscisic acid causes seeds to remain dormant during winter
(c)(i) Shoot: if auxin diffuses down the shady part of the plant, it makes the shady part grow longer than the light part of the plant. Therefore, the plant bends towards the light.
Root: When a plant is placed horizontally, the bottom part of the plant has more auxin. This makes the top side of the root grow more than the bottom and therefore the plant grows in response to gravity and is anchored into the soil.
(ii) Shoot: Phototropism. One part of the plant has light shining on it and one doesn’t.
Root: Geotropism. The plant is placed horizontally, so the auxin remains in the bottom part of the plant.
(d) 1. Can be used as rooting powders
2. Used in tissue culturing to grow new plants.
Q6. (a) X: Bowman’s capsule
Y: Distal convoluted tubule
(b) The target area should be connected to the distal convoluted tubule and the collecting ducts
(c) ADH makes the target area more permeable to water, so that more reabsorbtion of water can occur
(d) Blood volume decreases due to a decreased water concentration in the blood
(e) Produced in the hypothalamus, secreted from the pituitary gland
(f) Kidney transplant
Q7. (a)(i) So that other people can benefit from their research and continue the research further, aiding further scientific discovery
(ii) Repeat the experiment a number of times and ensure that they get the same result each time
(b) (i) 1. Use a pH buffer
2. Use a water bath
(ii) 1. Carbon dioxide
2. Iodoform test – sodium hydroxide and potassium iodide
(iii) 1. Multiply the power of the eyepiece by the power of the objective lens used
2. Adjust the diaphragm
(iv) 1. To ensure that a translucent stain is formed and that the paper is not simply wet
2. Test for a reducing sugar
Q8. (a)(i) Stroma of the chloroplast
(ii) Light is not required
(b)(i) Elodea (pondweed)
(ii) It is an aquatic plant, so the rate of photosynthesis can easily be seen as bubbles are produced from the plant
(iii) Count the number of bubbles per minute
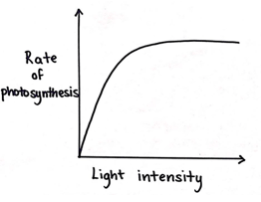
(iv)
(v) The rate of photosynthesis increases as light intensity (or carbon dioxide concentration) increases, until a stage when the plant is saturated with light and the graph levels off.
Q9. (a)(i) Rhizopus
(ii) Reproduces by sporulation / it is multicellular
(b)(i) -Flame a forceps
-Wash your hands with aseptic soap
-Wipe down the desk with disinfectant
(ii) Malt agar
(iii) -Stick the leaf to the top of the petri dish with some petroleum jelly
-Seal the dishes with parafilm
-Incubate the dishes upside down for 3-4 days at a temperature of 25°C
(iv) Pink colonies were present
(v) The area from which the leaves were collected had a high level of air pollution
Q10. (a)(i)
(ii) Tertiary consumers
(iii) Very little energy (10%) is transferred from one level in a food chain to the next one
(b)(i)
-Famine decreases the size of the human population.
-War decreases the size of the human population.
-An outbreak of a disease can decrease the size of the human population.
(ii) -Organisms have different adaptations in order to protect themselves from being preyed on and for survival.
-Organisms can have behavioural adaptations, e.g. birds migrate in the winter to protect themselves from adverse environmental conditions.
-Organisms can have physical adaptations, e.g. frogs have green-coloured skin so that they can blend in with their habitat and they are camouflaged so it is not easy for predators to see them.
(iii) -Conservation is the wise management of natural resources.
-Conservation is important in order to prevent the extinction of organisms
-An example of conservation in fisheries is using a large mesh size in order to allow small fish to swim free
(c)(i) Capture-recapture method
-On the first day, collect 30 snails.
-Mark them in a way that does not endanger them or make them more visible to predators
-Release the snails
-On the second day, collect 30 snails.
-Count how many of them are marked.
-The size of the population can be estimated using the following formula:
(Number caught and marked on the first day × number caught on the second day) ÷ number marked on the second day
(ii) Ecosystem: woodland
Plant: daffodil
Factors: -Temperature
-Light intensity
(iii) Temperature: using a thermometer
Light intensity: using a lux meter
Q11. (a)(i) -Carbon dioxide
-Oxygen
(ii) Carbon dioxide: all body cells where respiration occurs
Oxygen: at the alveoli
(b)(i)
(ii) 1. Location: In the wall of the right atrium.
Role: Sends impulses to the atria, causing them to contract. Also stimulates the AV node.
2. Location: In the wall of the heart, between the right atrium and the right ventricle.
Role: Sends impulses down the septum to the ventricles, causing the ventricles to contract.
(iii) The force of the blood on the arteries when the heart is in systole (contracted) and diastole (relaxed)
(c)(i) 1. Carries nerve impulses towards the cell body
2. Carries nerve impulses away from the cell body
3. Provides energy so that nerve impulses can be transmitted
(ii) -The nerve impulse reaches the neurotransmitter swellings and stimulates neurotransmitters to be secreted.
-Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft and form weak bonds with receptors on the post-synaptic neuron.
-The neurotransmitters are digested by enzymes and absorbed back into the pre-synaptic neuron so that they can be re-used.
-The electrical impulse is transmitted onwards
(iii) The myelin sheath insulates the electrical impulses, so that they can jump from one node to another, speeding up the impulse.
If the myelin sheath was not present the impulse would have to travel along the whole neuron.
Q12. (a)(i) -Breaking down a sugar fully requires energy and oxygen and is a long process.
-ATP allows energy to reach cells much more rapidly.
(ii) Nitrogenous base: adenine
Sugar: ribose
(b)(i) C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
(ii) 1. Glycogen
2. Liver
(iii) Pyruvate molecules break down into carbon dioxide and 2-carbon molecules called Acetyl CoA.
(iv) -ATP
-NADH
-Carbon dioxide
(v) ATP: used as an energy carrier for cellular reactions
NADH: provides electrons for the electron transport chain
Carbon dioxide: is released into the atmosphere by the lungs
(vi) Oxygen
(c)(i) Induced fit model
-The active site of an enzyme can only join with a particular substrate
-The active site changes shape slightly to accommodate the substrate
-An enzyme substrate complex is formed
(ii) What: The enzyme activity is decreased when compared to the maximum rate
Explain: The active site changes shape slightly and the bonds that are formed with the substrate are not as effective
(iii) -Sodium alginate
-Calcium chloride
(iv) -The enzymes can be reused
-A purer product is formed
Q13. (a)(i) Viruses
(ii) -Ribosome
-Cytoplasm
(b)(i) Law of Segregation: Inherited characteristics are controlled by pairs of alleles. At gamete formation, pairs of alleles split so that only one allele from each pair enters the gamete
Law of independent assortment: Either one of a pair of alleles is equally likely to combine with either one of another pair of alleles
(ii) T – tall
t – dwarf
Y – yellow
y – green
Parent genotypes: ttyy × TtYy
Gametes: ty × TY, Ty, tY, ty
(iii) There would be less variation of genotypes formed, as the genes for height and seed colour would be transferred on the same chromosome
(c)(i) The genetic changes in a population over time in response to the environment
(ii) -There is competition between species
-The more adapted members survive (survival of the fittest)
-The organisms that do not have the adaptation die
-The adapted members interbreed and pass on this adaptation to the offspring
-This gives the offspring the adapted genotype
-Over time this adaptation becomes more common
-The genotype of the population has changed
(iii) fossils: more modern fossils are more complex, showing that there have been changes in the genotypes of the population, causing the population to have different characteristics and features
Q14. (a)(i) Dispersal: a seed is transferred away from the parent plant
Suggest: -For colonisation to occur
-To reduce competition
(ii) Horticulturists can break dormancy by placing seeds in the fridge or breaking the testa before planting the seed in order to break dormancy
(iii) -Oxygen
-Suitable temperature
(iv) Digestion: in order to make nutrients absorbable and transportable
Respiration: provides the seed with energy
(v) 1. Mass decreased due to food stores being used up in respiration
2. Mass increased as the peas grew leaves that began to photosynthesise, increasing the mass of the food stores
(vi) Glucose
(b)(i)
(ii) Most chloroplasts are located here as there is more light shining on this part of the leaf, which provides the plant with more energy for the light stage of photosynthesis
(iii) -The leaf has air spaces, which means that the carbon dioxide that is needed for the dark stage can easily diffuse into the leaf
-The leaves have a large surface area so that a lot of light can be absorbed for photosynthesis
(iv) -Carbon dioxide
-Oxygen
-Water vapour
(v) Carbon dioxide
(c)(i) A gland that is ductless and secretes its products directly into the blood
(ii)1. Insulin
2. Islets of Langerhans
3. Fat and muscle cells, cells in the liver
4. Controls blood glucose levels
(iii) -Low levels of thyroxine cause the pituitary gland to produce TSH.
-This causes more thyroxine to be produced in the thyroid.
-If thyroxine levels are normal, TSH is not produced
(iv) -Diabetics use insulin injections to control their blood glucose levels
-Anabolic steroids can be used after injury in order to build up muscle
Q15. (a)(i) Beneficial: Bacteria are used to make food products, such as yogurt
Harmful: Bacteria cause illnesses, such as strepthroat
(ii)1. Binary Fission
2. -The loop of DNA replicates
-The DNA attaches to the cell membrane on opposite sides of the cell
-The cell elongates
-The cell splits into 2 identical cells, with each of the cells having a loop of DNA
(iii)1. The growth of cells in a closed container, where nutrients are added at the start and products are removed at the end
2. -Not all bacteria may be killed by the antibiotics
-The ones that do not die are now adapted
-They reproduce and give this adaptation to their offspring
-Over time, large numbers of adapted bacteria are present and they can no longer be killed by the antibiotic
(iv) They form endospores
(b)(i) -Bile is needed to neutralise chyme, which is acidic.
-Bile salts are alkaline and so they neutralise the acids in chyme.
(ii) -Active immunity involves the production of antibodies.
-Memory B and memory T cells will then remember the antigens for a long time and more antibodies will be produced if the disease in encountered at a later stage.
-Therefore, long-lasting immunity develops.
(iii) -When we exercise, we heat up.
-Sweat carries this extra heat out of the body when it evaporates so that the body’s temperature can stay constant.
(iv) -Antibiotics are used to kill bacteria and fungi.
-Influenza is a virus.
-Viruses cannot be killed by antibiotics.
(v) -High sugar/salt concentrations have a lower water concentration than the cytoplasm of bacteria.
-Therefore, water exits the bacteria by osmosis.
-This dehydrates the bacteria, killing or inactivating them.
(c)(i)1. Name: vitreous humour
Role: Maintains the shape of the eye
2. Name: rods and cones
Role: detect colours so that they can later be converted to electrical impulses
3. Name: conjunctiva
Role: protects the eye
(ii) We have a greater field of vision
(iii) Name: glue ear
Corrective measure: grommets are inserted into the ear